Contents
Do you think a single phase system is better just because it’s simpler? That’s a common misconception. Whether you’re working on a residential setup or planning an industrial expansion, understanding the difference between a three phase system and a single phase system can save you time, money, and a lot of frustration. In this article on the Tech4Ultra Electrical website, I’ll walk you through the real pros and cons of each system—and help you choose the right one with confidence.
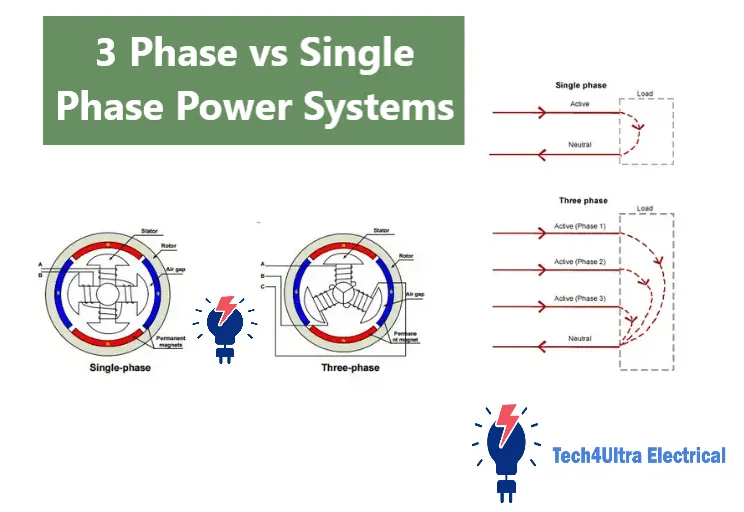
When it comes to electrical power distribution, two systems dominate the field: the single phase system and the three phase system. Each has its own unique structure, use cases, and performance characteristics. A single phase system uses just one alternating current (AC) waveform, commonly found in residential homes and small businesses. In contrast, a three phase system uses three separate AC waveforms that are offset in phase, making it ideal for delivering higher power efficiently—typically in industrial and commercial settings.
The purpose of comparing these two systems isn’t just academic—it’s practical. Choosing between a single phase system and a three phase system can directly impact your project’s efficiency, cost, and scalability. Whether you’re wiring a home or powering up a factory, knowing the advantages and limitations of each system helps you make smarter, more informed decisions.
Understanding their roles in both industrial and residential environments is key. A household setup doesn’t need industrial-level voltage, but a production plant can’t run efficiently on residential wiring. This comparison lays the foundation for selecting the right electrical infrastructure for your needs.
Overview of Power Systems
1. What is a Single Phase System?
A single phase system is the most basic type of AC electrical distribution. It uses a single alternating voltage cycle delivered through two wires: one live (or hot) wire and one neutral. The voltage alternates between positive and negative peaks, typically at 50 or 60 Hz depending on your country.
This system is very common in residential buildings. It’s perfect for powering lights, small appliances, and standard outlets. The simplicity of the single phase system makes it easy to install and maintain, but it does have limitations—mainly in how much power it can carry efficiently.
Power flow in a single phase system is unidirectional at any given moment. Since the power returns to zero every half cycle, the energy delivery isn’t constant, which can cause fluctuations under heavy load.
2. What is a Three Phase System?
In a three phase system, power is delivered via three alternating currents, each phase offset by 120 degrees. This creates a continuous and balanced flow of energy that never drops to zero. It uses either three or four wires—three hot wires (phases) and optionally a neutral.
This system is ideal for high-demand environments like factories, large motors, and commercial buildings. It’s more efficient in energy transmission and better for running heavy machinery with minimal vibration or power dips.
The balanced nature of a three phase system also means lower conductor size for the same load compared to single phase. It’s an upgrade in power delivery, stability, and cost-effectiveness for large-scale applications.
Read Also: Electric Power System: Key Parts and How It Works
Technical Comparison: Three Phase vs Single Phase
Choosing between a three phase system and a single phase system comes down to understanding how they handle electricity. Let’s break it down technically so it actually makes sense—no engineering degree required.
Voltage, Current, and Power Delivery: A single phase system typically delivers 230V in many regions (or 120V in North America), while a three phase system can supply 400V or more. More voltage means more power—and with three phases working together, power delivery is smoother and more continuous in the three phase system. You get higher output with less current, which means less stress on wires and devices.
Equipment Size and Efficiency: Because of the consistent power flow, equipment like motors and transformers in a three phase system are usually more compact and efficient. A three-phase motor, for instance, produces more torque with the same amount of input power compared to a single-phase one. On the other hand, a single phase system requires larger motors for the same job—and they tend to run hotter and vibrate more.
Installation Complexity: Setting up a single phase system is straightforward. Two wires, a breaker, and you’re good to go. But a three phase system? It needs more planning—three or four wires, balanced loads, and often professional setup. It’s not DIY-friendly unless you’re a qualified electrician.
Cost Implications: Initially, a single phase system is cheaper. Less wiring, simpler devices, lower setup costs. But for long-term industrial use, a three phase system becomes more economical due to lower operating costs, reduced energy losses, and better equipment lifespan. So while you might pay more upfront, the efficiency pays off over time.
In short, if you’re powering a home, go single phase. If you’re powering a warehouse, go three phase. Matching the system to your needs is what really matters.
Advantages of Three Phase System
When I first worked with a three phase system, I was honestly surprised by how much smoother and more efficient everything ran. If you’re still on the fence about upgrading from a single phase system, here’s why the three-phase setup is a game changer—especially for industrial applications.
Constant Power Flow: Unlike a single phase system that hits zero volts twice every cycle, a three phase system maintains a steady flow of power. That means no pulsing, no dips—just continuous energy. This is a huge advantage for equipment that needs consistent performance like motors, compressors, and large pumps.
Higher Power Density: With three lines sharing the load, the three phase system can transmit more power using the same amount of current. This makes it ideal for environments where high power output is needed without overloading the infrastructure.
Better Load Balancing: The beauty of a three phase system lies in its ability to distribute loads more evenly. Each phase carries part of the total current, which reduces the chances of system overload and improves overall reliability.
Smaller Conductor Size: Since current is shared across three conductors, wire sizes can be smaller than what you’d need in a single phase system for the same power delivery. This might seem like a minor detail, but over long distances, it makes a huge difference in cost and installation ease.
Improved Voltage Regulation: Voltage drops are a common problem in long cable runs. However, in a three phase system, the voltage remains more stable, especially under variable load conditions. That’s critical for sensitive equipment and automation systems.
Higher Starting Torque: If you’ve ever tried to start a heavy-duty motor on a single phase system, you know the struggle. A three phase system provides much higher starting torque, which helps motors get up to speed faster and more efficiently.
Lower Power Loss: Because power is delivered more efficiently in a three phase system, there’s less energy wasted as heat. That means lower energy bills and less strain on your electrical infrastructure.
Lower Maintenance and Operational Cost: Equipment running on a three phase system tends to last longer and require fewer repairs. Why? The balanced load, lower heat generation, and efficient power delivery reduce wear and tear significantly.
Bottom line? If you’re serious about performance, reliability, and long-term savings, the three phase system offers advantages that a single phase system simply can’t match.
Watch Also: Top Electrical Engineering Formulas You Must Know
Applications and Use Cases
The real strength of a three phase system shows up when we look at where it’s used. It’s not just a matter of “more power”—it’s about delivering power smartly and reliably, especially where stability is non-negotiable. If you’ve ever worked in facilities maintenance, industrial engineering, or commercial development, you’ve likely seen the three phase system in action without even thinking about it.
Industrial Motors: This is the number one domain for the three phase system. Motors used in manufacturing—whether for conveyor belts, pumps, or CNC machines—rely on the consistent torque and efficiency this setup provides. The high starting torque and minimal vibration are critical in keeping production lines smooth and maintenance costs low.
HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning in large buildings need a reliable power source. A three phase system supports the heavy compressors and blowers that simply wouldn’t run efficiently—or at all—on a single phase system. In fact, most commercial HVAC specs require three-phase compatibility by default.
Power Transmission Grids: National and regional grids operate almost entirely on three phase systems. The reason? Long-distance transmission is far more efficient. Power loss is lower, voltage regulation is tighter, and the infrastructure handles large loads without breaking a sweat.
Large-Scale Commercial Buildings: Shopping malls, office towers, and stadiums all rely on three phase systems. They power elevators, escalators, lighting systems, and centralized HVAC. The load balancing prevents spikes and failures that could disrupt thousands of people.
Data Centers: These facilities are the backbone of modern digital infrastructure. They can’t afford power fluctuations. The three phase system provides clean, stable energy to thousands of servers, cooling systems, and backup equipment—where uptime is mission-critical.
In short, anywhere you need efficiency, reliability, and serious power handling, the three phase system is the go-to choice. The single phase system just isn’t built for this scale.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
One of the lesser-known but most valuable aspects of the three phase system is its contribution to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. While many focus on its industrial power and reliability, this system also has a green side—especially when compared to a single phase system.
Reduced Energy Losses: Because power is delivered more evenly and continuously in a three phase system, electrical losses due to resistance in wires and components are significantly lower. Less wasted energy means better performance and reduced electricity bills, particularly in large-scale operations.
Material Savings: You also save on materials. Since the current load is distributed across three conductors, the size of each conductor can be smaller compared to what’s needed in a single phase system. That translates into less copper, less insulation, and overall lighter infrastructure—cutting down on raw material use and cost.
Impact on Carbon Footprint: Every watt saved matters. By minimizing energy waste and optimizing load efficiency, a three phase system can help reduce the carbon footprint of buildings and industries. This might not be obvious at first glance, but over time, the environmental benefits add up—especially when powering factories, hospitals, or data centers around the clock.
If you’re thinking long term—not just about today’s costs but tomorrow’s impact—the three phase system clearly supports a more sustainable energy strategy.
Real World Scenarios: When to Choose Three Phase or Single Phase
Here’s where things get practical. You’re planning a project and need to decide—three phase system or single phase system? It’s not just about the specs. It’s about your actual needs, budget, and long-term goals. So let’s break it down with real-world context.
Residential vs Industrial Decisions: For homes, a single phase system is more than enough. It powers everything from lights and TVs to refrigerators and air conditioners. But the moment you enter the industrial or commercial world—workshops, bakeries, clinics—you’re likely going to need the continuous power delivery and efficiency of a three phase system. Machines, large motors, or heavy loads? Go three-phase.
Startup vs Expansion Planning: If you’re launching a small business or setting up a temporary site, starting with a single phase system can help keep initial costs low. But if you anticipate scaling up—like adding machinery, expanding floor space, or increasing load—it’s smarter to invest early in a three phase system. It’s painful (and expensive) to upgrade infrastructure later.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: A single phase system wins in simplicity and installation cost. Less wiring, smaller breakers, cheaper equipment. But if you compare over a 5–10 year timeline, the three phase system usually comes out ahead. You save on maintenance, power loss, and get higher efficiency from motors and devices. Plus, you open the door to future upgrades without redoing everything.
My personal rule? If the power demand stays under 10 kW and won’t grow much—stick to single phase. But if you’re building for the long haul, or your equipment list includes industrial-grade tools, invest in a three phase system from the start. You’ll thank yourself later.
Challenges and Considerations of Three Phase Systems
While the three phase system has plenty of advantages, it’s not without its drawbacks. It’s important to be realistic about the challenges, especially if you’re weighing it against a single phase system for a small-scale project or residential use.
Higher Initial Setup Cost: This is the most obvious hurdle. Installing a three phase system involves more wiring, larger panels, and more expensive circuit breakers. The cost of upgrading your electrical service—especially if you’re converting from single phase—can be significant. It’s a long-term investment, but that upfront bill might sting.
Need for More Complex Protection Devices: With more power and more conductors comes more responsibility. Protecting a three phase system requires advanced relays, surge protection, and monitoring systems. That adds layers of complexity and ongoing maintenance compared to a basic single phase system.
Limited Availability in Residential Areas: If you’re in a residential zone, you may not even have access to a three phase system. Utility companies often restrict it to commercial or industrial zones. Even if you want it, you may face extra charges or need special approvals.
In short, a three phase system isn’t always the right fit—especially when dealing with smaller loads or tight budgets. It’s powerful, but it’s not plug-and-play. Know your needs before you commit.
Watch Also: System of Wiring: Types, Uses, and Tips
Expert Recommendations and Industry Insights
Talk to any experienced electrical engineer or facility manager, and you’ll hear a recurring theme: for long-term reliability and scalability, the three phase system is hard to beat. It’s not just about more power—it’s about smarter power delivery.
According to a 2023 industry report from IEEE, over 80% of new industrial facilities are now built with a three phase system by default. This trend isn’t slowing down. As automation, data centers, and EV charging infrastructure expand, the demand for high-efficiency power systems is growing fast.
Experts like Dr. Steven Mallory, a consultant in industrial energy systems, point out: “The future of power systems is rooted in modular, three-phase architecture. Even in smaller commercial settings, we’re seeing a shift toward three-phase solutions due to the rise in power-sensitive digital equipment.”
Even residential architecture is catching up. In parts of Europe and Asia, new apartment complexes are being designed with optional three phase system panels, anticipating future high-load appliances like heat pumps, home EV chargers, and battery systems.
Looking ahead, the future is clearly leaning toward more adaptable, resilient energy frameworks. While the single phase system will continue to serve smaller households just fine, three-phase electric power is becoming the backbone for modern infrastructure—especially as energy demands rise and sustainability becomes a priority. Its efficiency, reliability, and scalability make the three phase system the go-to choice for powering the future.
Conclusion
By now, you’ve seen just how different a three phase system is from a single phase system—not just in power, but in purpose. We covered the core differences in design, efficiency, installation, and cost. We looked at where each system fits best: homes, factories, data centers, and everything in between.
If you’re working with low power needs and want to keep things simple, a single phase system is still a solid option. But if your project involves growth, heavy machinery, or demands continuous performance, then the three phase system is the smarter, more future-proof investment.
At the end of the day, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. The best system is the one that fits your specific use case, budget, and long-term plans. Think practically, plan ahead—and don’t hesitate to consult with an electrical professional before making a decision.
FAQs
What are the advantages of three-phase system over single-phase system?
A three phase system delivers continuous power, higher efficiency, and better load balancing compared to a single phase system. It’s ideal for industrial applications where consistent energy is essential, and it also supports smaller conductor sizes and lower maintenance over time.
What is an advantage of three-phase generation over single-phase generation?
One major advantage is the constant power flow. Three-phase generation produces power that never drops to zero, making it more stable and efficient than single-phase generation. This consistency is crucial for running motors and large electrical systems smoothly.
Why do we prefer 3 phases instead of single phases?
We prefer three phases because they support higher loads with less current, reduce voltage drops, and offer superior performance for heavy-duty equipment. In contrast, a single phase system is more limited and better suited for basic residential use.
What is the advantage of three-phase star systems over single-phase star systems?
A three-phase star system provides more flexible voltage options and improved fault tolerance. It also allows for both line-to-line and line-to-neutral connections, giving it a major advantage over a single-phase star system in both power handling and safety.

1 thought on “What Is Clamping Voltage? How It Protects Your Devices”